Kafka Partition
In Apache Kafka, a partition is a unit of parallelism and scaling for topics. Each topic in Kafka can be split into one or more partitions, and each partition can be located on a different broker in the Kafka cluster.
A partition is an ordered and immutable sequence of records that are stored on disk on a broker. All messages published to a partition are assigned a unique sequential ID called the offset. This offset is used by Kafka to track the position of a consumer in a partition.
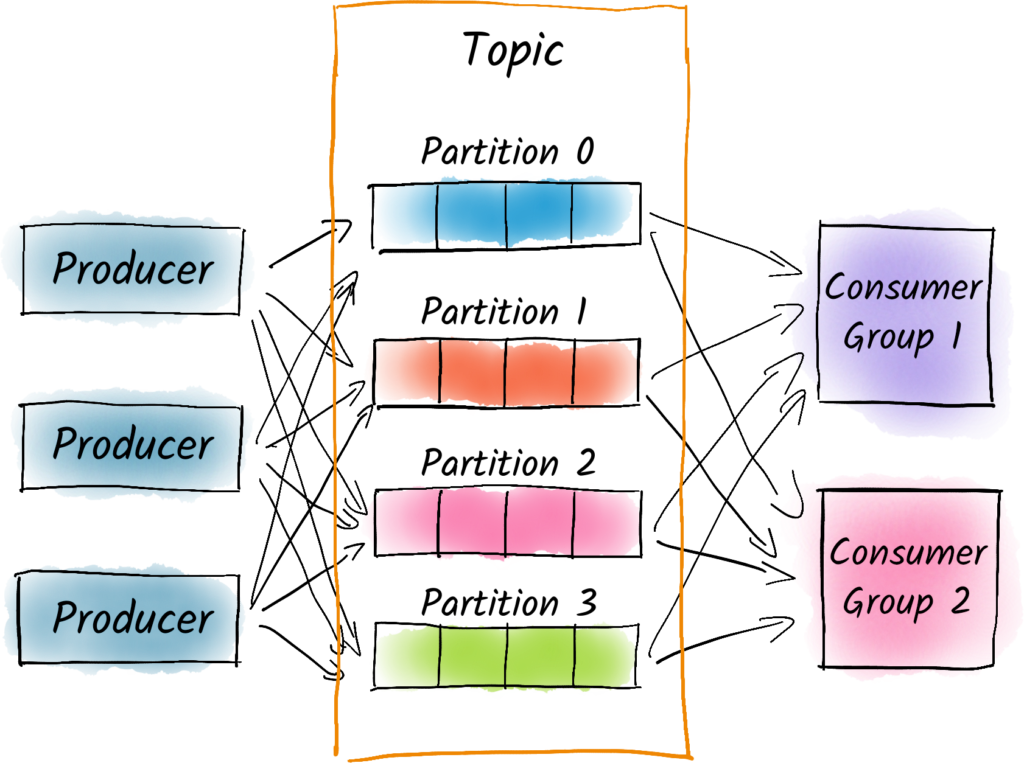
By partitioning a topic, Kafka enables parallel processing of data across multiple consumers. Each consumer can read from a different partition, allowing for high throughput and scalability. Partitioning also allows for fault tolerance, as replicas of each partition can be stored on multiple brokers to provide redundancy.
Kafka provides a flexible partitioning strategy that allows developers to control how data is distributed across partitions. By default, Kafka uses a hash-based partitioning strategy, where messages are assigned to partitions based on the key of the message. This ensures that messages with the same key are always assigned to the same partition, which can be useful for maintaining order or grouping related messages.
Developers can also define their own custom partitioning strategy based on the application requirements. For example, a partitioning strategy might be based on the geographic region of the data source, or the user ID of the data consumer.
Overall, partitions are a fundamental concept in Kafka that enable scalable and fault-tolerant processing of data. By partitioning topics, Kafka provides a powerful and flexible way to process large amounts of data in parallel across a distributed system.